OSPF - Virtual Links

Two or more separated area zeros creating a discontiguous area zero or an area that can not connect directly to area zero and needs to go through a transit area to get back to area zero.
Virtual links are a control plane tunnel to bridge areas, you could also use any data plane tunnel.
Primary Issues:
- If there is no area 0, the router will not consider itself an ABR
- If there is an area 0, the router will consider itself an ABR. OSPF loop prevention will be in effect that a type 3 LSA is not allowed to be used (routing bit is not set) if it arrives on a non-area 0 interface
Virtual links (VLs) are used to correct specific area issues
- Areas that are not connected to area 0
- Repairing a discontiguous area 0
- Virtual links should be used to correct temporary situations, such as outages and mergers
- Virtual links can only traverse a normal area
- Virtual links can only traverse one area at a time, but can be chained together
- Virtual links are always a member of area 0
- If area 0 is authenticated, the key needs to be put on the virtual link
- Virtual links are run as a demand circuit, hellos are suppressed, and the database is not refreshed. DNA (Do Not Age) is set on updates received across the virtual link
- Virtual links are configured between router IDs, not IP addresses
Inactive Area (0) - No neighbors, allows type 3 LSAs to arrive on a non-area zero interface
Virtual link is set in the area it is transiting through, use the router ID, not the IP address.
router ospf 1
area 100
virtual-link 10.2.2.2
message-digest-key 1 md5 PASSWORD
show ip ospf virtual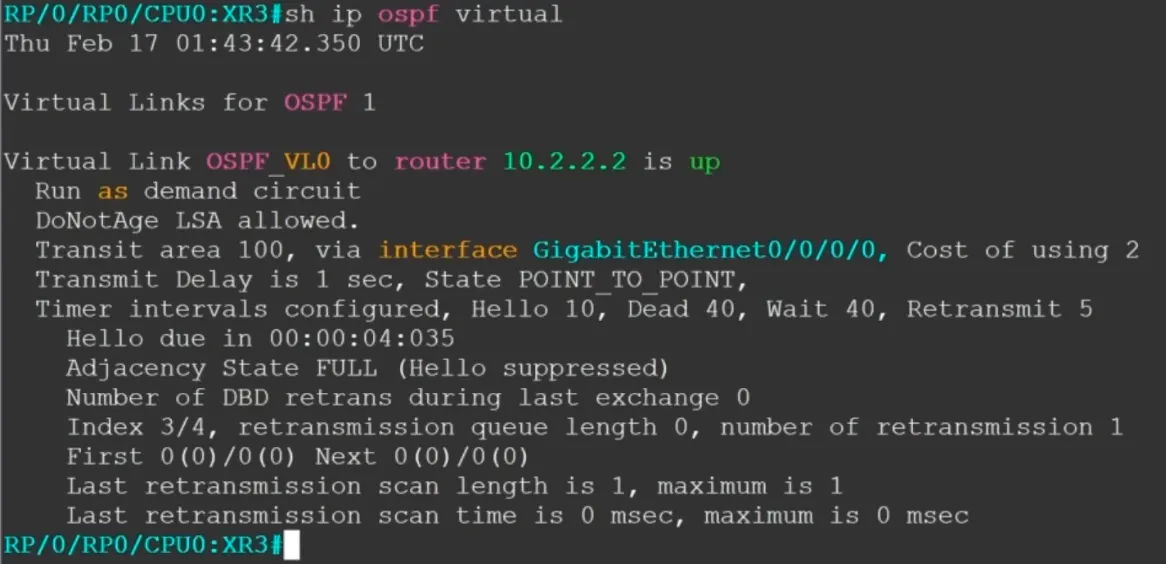
Virtual link shows as up if the router ID is in the database, but the virtual link may not be up. Check the Adjacency state shows as FULL
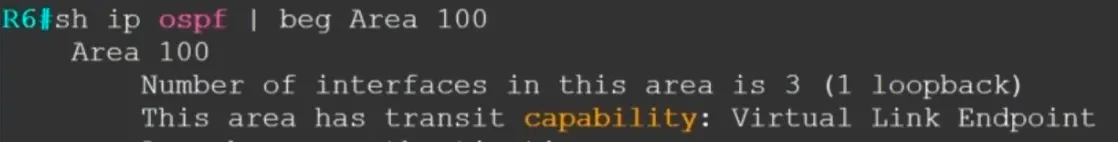
Capability Transit
Not supported on IOS-XR. On by default on IOS-XE.
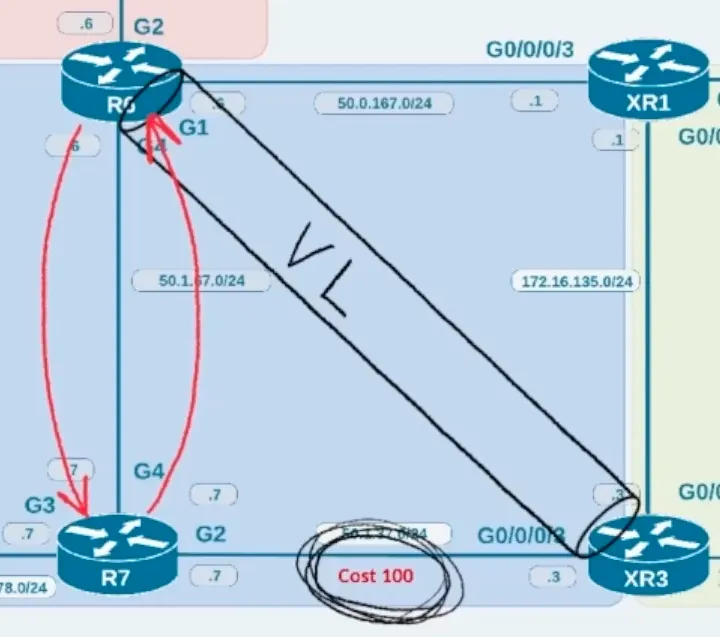
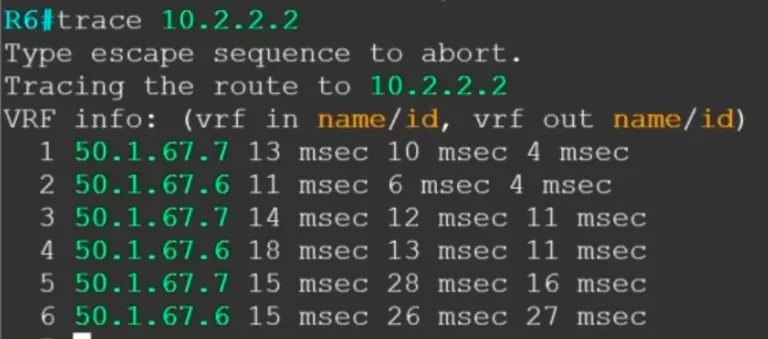
Use the best OSPF path, not following the path of the virtual link. Ideally, the virtual link should be built on the best path to avoid this.
router ospf 1
no capability transitAs the virtual link is only a control plane tunnel, this could create a loop if the router is not following the best path.
Using a GRE tunnel
GRE uses IP protocol 47
Virtual link is part of OSPF, where a GRE tunnel is a separate solution
- The only requirement is IP reachability, usually using loopback interfaces
- Can run over any area type and over many areas
GRE tunnel interface is normally be put into area 0 to mimic a virtual link, but could be in the separated area to bring it back to area o.
int lo 100
ipv4 address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.255
router ospf 1
area 100
int lo 100
int tunnel-ip 1
tunnel soure lo100
tunnel destination 10.0.0.1
ipv4 address 172.16.12.2 255.255.255.0
no shut
router ospf 1
area 0
authentication message-digest
message-digest-key 1 md5 PASSWORD
int tunnel-ip 1
net point-to-point



