OSPF - Design Principles

- Number of neighboring routers - no more than 60
- Number of routers in an area - no more than 50
- Number of areas connected to a router - no more than 3
- The router acting as the DR should be the highest spec.
OSPF Area Design
- The amount of data in an area impacts OSPF performance
- Use STUB / TOTAL STUB areas where possible
- Areas should be designed around geography and functional boundaries
- Summarization minimizes route changes (Flapping) impact
- Large networks have only ABRs in area 0
- Contiguous, split-able addressing
Typical OSPF Hub and Spoke Design
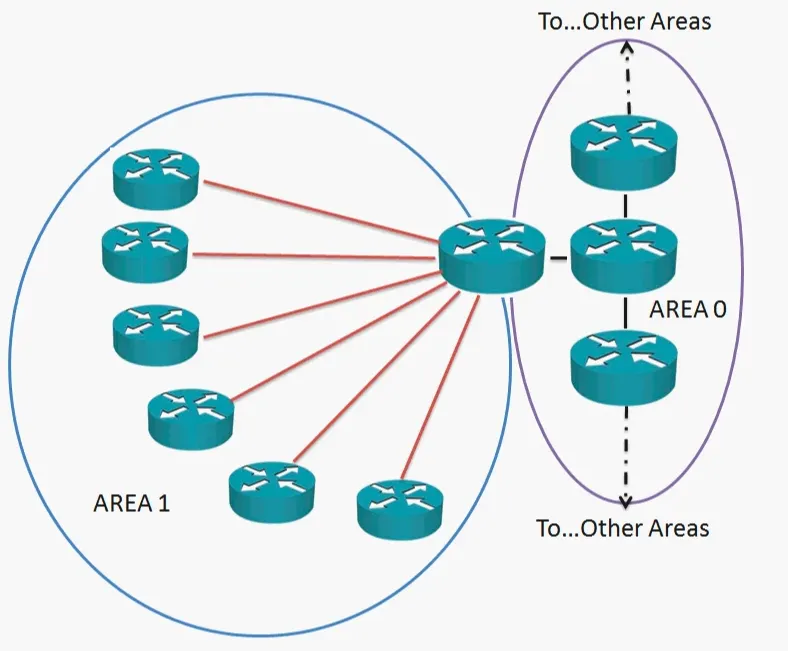
- Use STUB areas whenever possible
- Use NSSA to handle expansion oddities
- Area 0 ABRs are summary points
- Keep area 0 small and very stable
Improving OSPF convergence time
All protocols must detect, propagate, process, and update
Cisco implements OSPF Exponential backoff algorithm for LSA generation and SPF
LSA generation:
- LSA-START: Initial delay to generate LSA (0ms)
- LSA-HOLD: minimum time before flooding (5s, Increases Exponential)
- LSA-MAX-WAIT: maximum time to wait before flooding (5s)
SPF Algorithm:
- SPF-START: time to wait before initially running SPF
- SPF-HOLD: time between consecutive SPF runs
- SPF-MAX-WAIT: maximum time to wait between SPF runs




