Multicast
Allowing a single host to send a single stream of traffic to reach any number of destination hosts.
- PIM-DM - flood and prune
- PIM-SM - Explicit Join
- IGMP v1-v3
- IGMP snooping - layers 2 and 3
FF02::1 is the all-nodes multicast group within the scope of the local link. A packet with this destination address is received and processed by all IPv6-enabled interfaces.
The first 24 bits of a multicast MAC address are always 01:00:5E.
Link-local non-routable 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255 (reserved for local network use, has TTL = 1)
The multicast range 239.0.0.0/8 is equivalent to private addresses.
Multicast addresses in IPv6 use the prefix FF00::/8
well-known IPv4 multicast addresses
| 224.0.0.1 | All Hosts |
| 224.0.0.2 | All Routers |
| 224.0.0.4 | DVMRP Router |
| 224.0.0.5 | OSPF Routers |
| 224.0.0.6 | OSPF Designated routers |
| 224.0.0.9 | RIPv2 Routers |
| 224.0.0.10 | EIGRP Routers |
| 224.0.0.12 | DHCP server/relay agent |
| 224.0.0.13 | All PIM Routers |
| 224.0.0.18 | VRRP |
| 224.0.0.19 | All IGMPv3 Routers |
| 224.0.0.102 | HSRP |
| 224.0.0.107 | PTP v2 |
| 224.0.0.251 | mDNS |
| 224.0.0.252 | LLMNR |
| 224.0.0.253 | Teredo |
| 224.0.1.39 | RP announce group |
| 224.0.1.40 | RP discovery group |
well-known IPv6 multicast addresses
| ff02::1 | All Hosts |
| ff02::2 | All Routers |
| ff02::5 | OSPF Routers |
| ff02::6 | OSPF Designated routers |
| ff02::8 | IS-IS Routers |
| ff02::9 | RIP Routers |
| ff02::a | EIGRP Routers |
well-known Ethernet multicast addresses
| 01-80-C2-00-00-00 | STP 802.1D |
| 01-00-0C-CC-CC-CC | CDP, VTP |
| 01:00:0C:CC:CC:CD | Cisco per-VLAN STP |
Source Trees
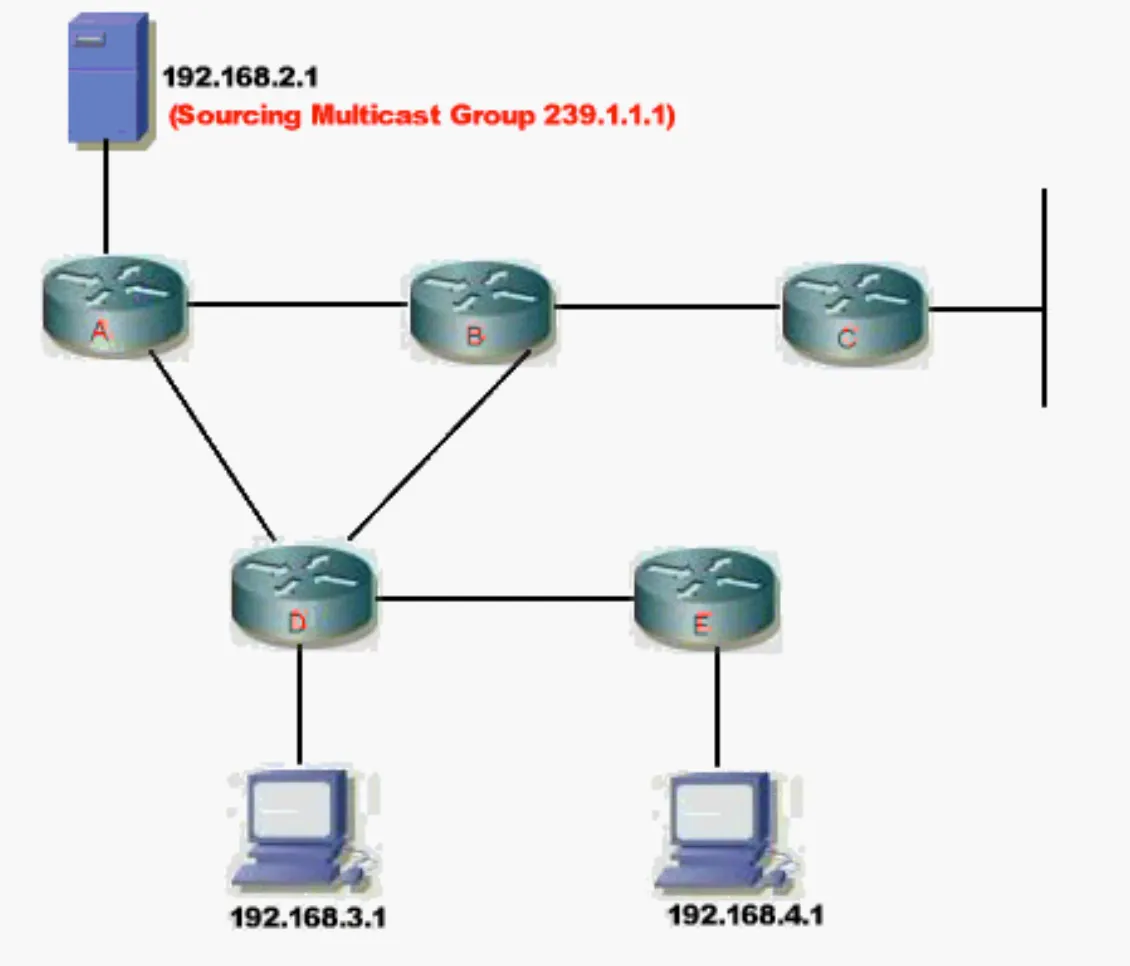
Routers examine the Source IP address and the Multicast group. Create an entry to the multicast routing table.
All routers are aware of the stream. Not scalable for large networks.
Shared Trees
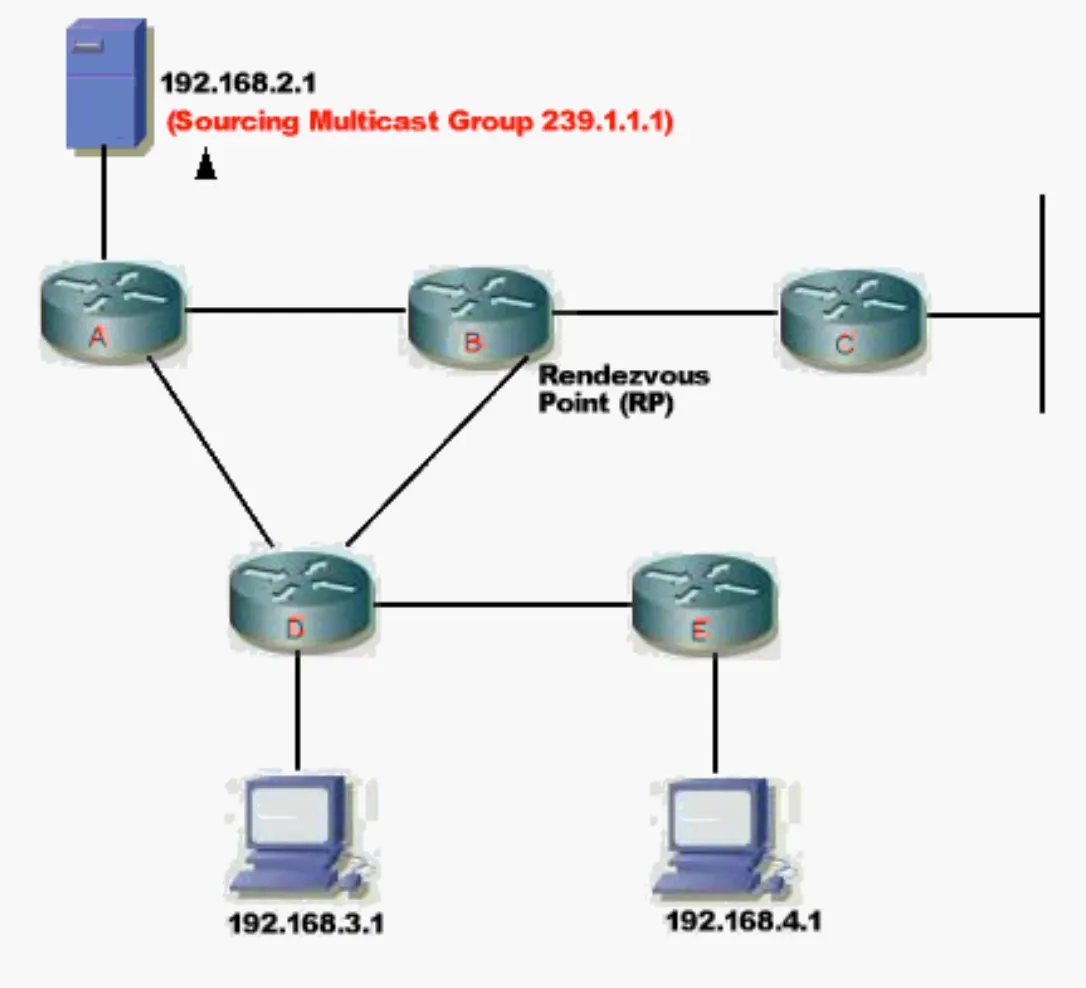
Multicast streams register with the RP router. Other routers have a default gateway to the RP.
Client wants to subscribe to a stream, router will ask the RP, RP will act as a proxy.
Router can switch back to teh source tree model if more efficient, once it has source from RP.
Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) Dense Mode
Relies on unicast routing table to get around network.
Source Tree model for small networks.
Enabled on all required interfaces on all routers
ip multicast-routing
int se0/0
ip pim dense-modeAll routers will get multicast stream and pass it on to all other routers.
Routers will prune back if no clients are requesting the stream. Resets itself every 3 minutes.
Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) Sparse Mode
Shared tree with a Rendezvous Point. Pull mode.
Everything goes to RP first, once router has the source may change if more efficant path to source.
sparse-dense-mode - runs in both modes, dense mode if no RP. Auto RP needs this mode.
Can use an access list to use a different RP for groups.
Auto RP to advise the RP without static configuration on all routers. Use a loopback interface.
scope is TTL of the RP advertisement. Default every 60 seconds.
Discovery router (mapping agent) collects all the RP advertisements and sends them out
ip multicast-routing
int se0/0
ip pim sparse-dense-mode
show ip pim interfaces
show ip mroute
#Test without multicast server
int e0
ip igmp join-group 230.140.100.1
ping 230.140.100.1
# Add RP on all routers as static configuration
ip pim rp-add 192.168.1.3
# Auto RP
ip pim send-rp-announce s0/0.1 scope 15
ip pim send-rp-discovery scope 15
ip pim accept-rp #add to all routers
show ip pim rp map
#Restrict multicast traffic
int se0/1
ip multicast ttl-threshold 255
ip multicast boundary 1
Switch configuration
By default multicast is sent to all ports.
ip igmp snoopingFrame Relay configuration
If broadcast is not enabled on frame-relay
int s0/0.1
ip pim nbma-mode



