MPLS

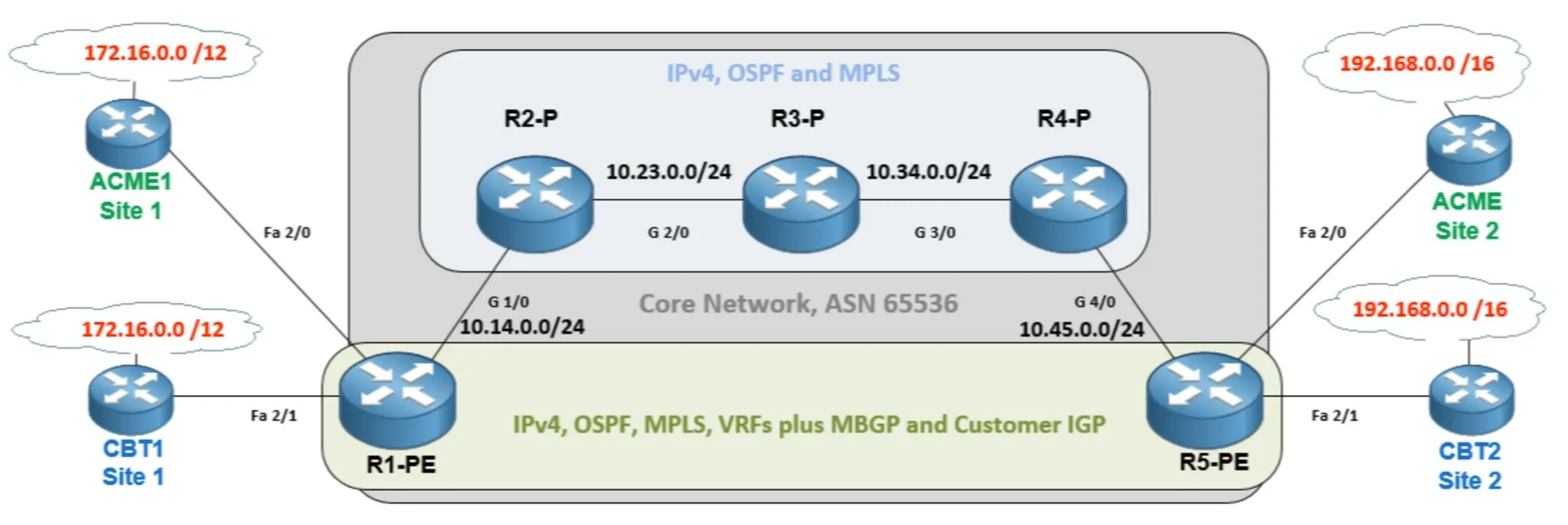
Router generates local labels for each network in the routing table, and advertises to adjacent routers.
MPLS labels are locally significant to the router
- A label is created for each IP destination
- Neighbors use the labels learned from their neighbors
- Labels of directly connected neighbors need to be known
LDP - Label distribution protocol
LSP - Label switch path
LSR - Label switch router
Labels added to packets at layer 2.5
Routers swap the label, don’t need to look at layer 3 information.
IPv6 can go over IPv4 network.
Labels are 32 bits
- 20 Bits Label
- 3 bit Experimental (QoS)
- 1 bit bottom of stack (set to 1, top/transit label set to 0)
- 8 bits TTL
Labels 0-15 are reserved
imp-null (3) Directly connected
PHP - Penultimate hop popping - remove label before it hits the final router. (Default)
mpls ip
int gi1/0
mpls ip
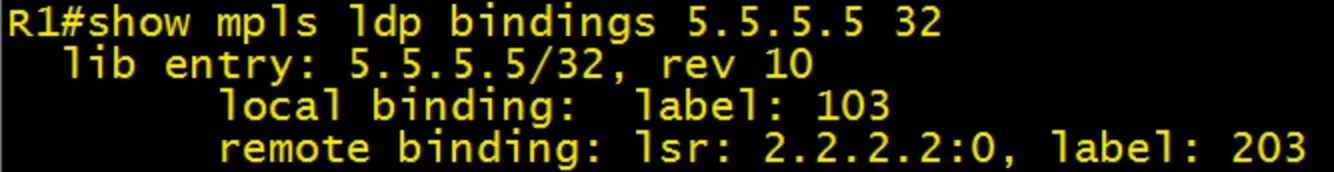
show mpls ldp bindings 5.5.5.5 32
show mpls forwarding-table 5.5.5.5Constrain range of labels: mpls label range 100 199

Transport Address
Router ID by default, is the transport address
- Configured
- Highest IP on loopback
- Highest IP on Interface
int g2/0
mpls ldp discovery transport-address interfaceVRF Utilities
ping vrf 101:ACME 172.16.101.2
traceroute vrf 101:ACME 172.16.101.2
traceroute mpls ipv4 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255
show ip route vrf 101:ACME
ip route vrf 101:ACME 10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.101.2MPLS Layer 2 VPNs
Service to allow Layer 2 connectivity between customer sites. * VPWS - Virtual Private Wire Service * Point-to-point connection * Can use L2TPv3 over an IP network * Can use MPLS for the transport (AToM) * AToM - Any Transport over MPLS * subset of VPWS * Supports Ethernet, PPP, HDLC, Frame Relay, and ATM. Advantages to

MPLS Layer 3 VPNs
* Routing protocol between PE and CE to learn customer routes * VRF - Virtual Routing and Forwarding * VPNv4 Route - Information added to routes to identify the customer * mBGP used to exchange VPNv4 routes between PE routers * No encryption on traffic PE to PE mBGP router bgp 65536 neighbor 5.5.







