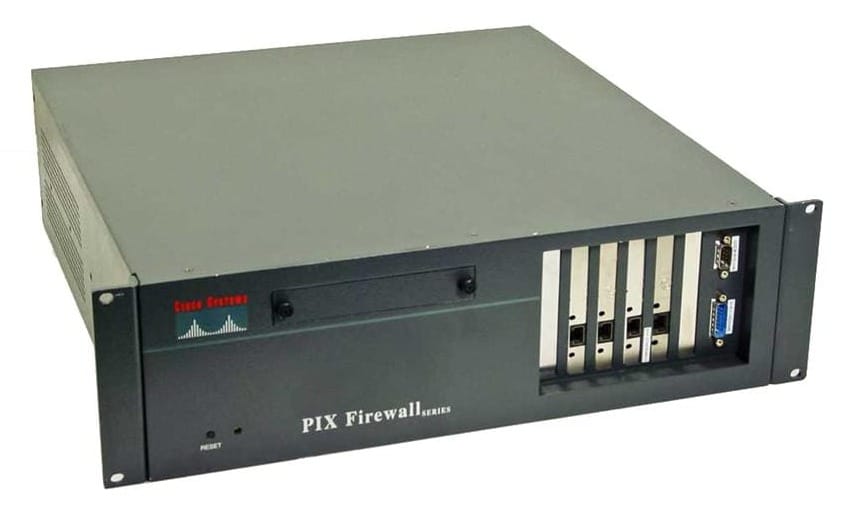
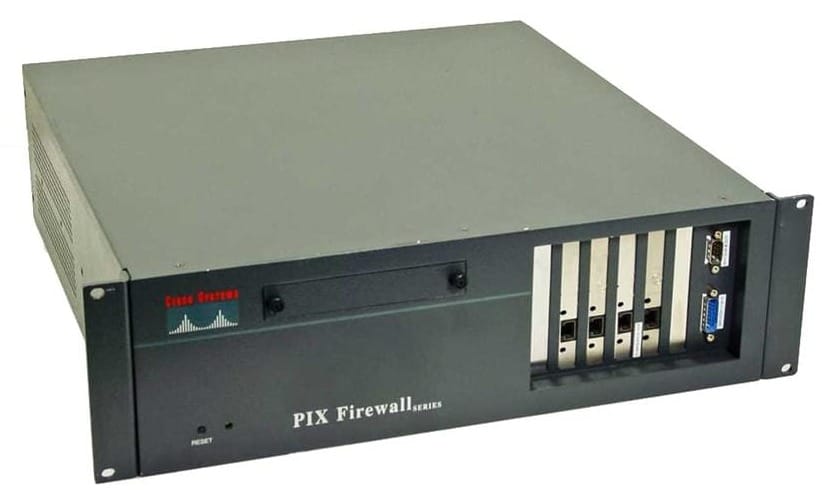
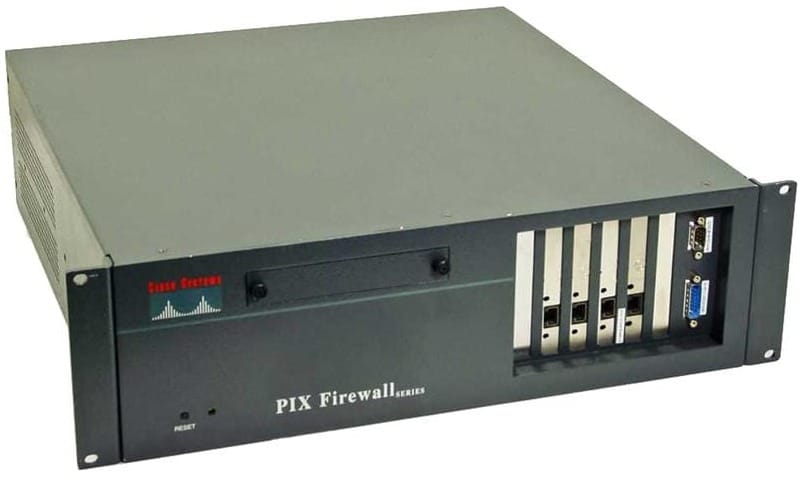
Digital Voice Ports

Digital ports allow for multiple calls
Digital Signalling
Channel Associated Signaling (CAS)
- Steals bits from user data for signaling
- Advantage: all channels are available for data
- Disadvantage: User bandwidth is reduced
Common Channel Signaling (CCS)
- Dedicates a single channel to signaling
- Advantages: more signalling information available, no user bandwidth used
- Disadvantage: lose a complete channel
ISDN
- Two versions of IDSN: BRI and PRI
- Standard-based signaling protocols
- Q.921 - Error Detections/Corrections (Layer 2)
- Q.931 - Call Setup/Teardown/information (Layer 3)
- Non-facility associated signaling (NFAS) allows a single D channel for multiple PRI interfaces
- QSIG (Based on Q.931) allows PBX-to-PBX interconnects
- The last channel 23 is the control channel for T1
- Channel 15 is the control channel for E1
show controllers t1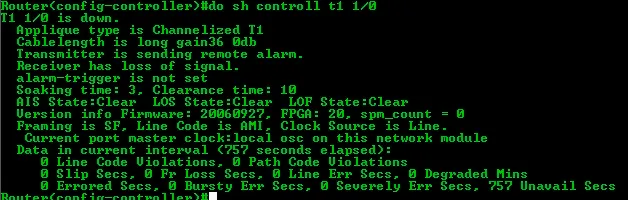
CAS Configuration
controller t1 1/0
no shut
ds0-group 1 timeslots 1-24 type fxo-ground-startCCS Configuration
isdn switch-type primary-5ess !!Needs to match provider
controller t1 1/0
no shut
pri-group timeslots 1-24 type fxo-ground-start
interface serial 1/0:23
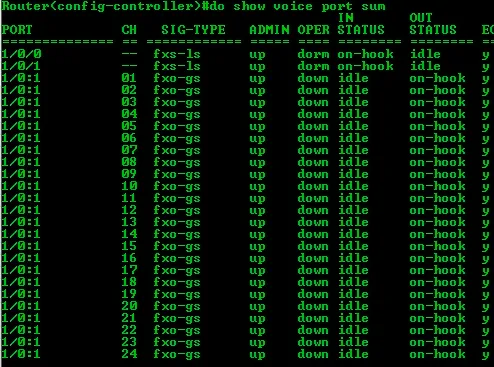
isdn incoming-voice voiceshow voice port summary